|
Current Trends in Intra
Uterine Fetal Surgery
Dr.Sameer Dikshit
MD, DGO, FCPS, FICOG
Introduction
Since a long time, mankind has
appreciated that our external environment has an effect on
the fetus. Ayurveda has suggested certain restrictions on
the mother for a healthy and intelligent progeny. However,
since the ancient man had no means of visualizing the fetus
and hence no means of visualizing abnormal fetus, the
interventions were only of preventive nature. It is only
after the advent of USG that the fetus and fetal
abnormalities could be seen before birth. This stimulated
medical science to devise ways to correct these defects.
History
Dr. Sir A.W. Liley is considered father
of intra uterine surgery. He carried out first intra uterine
transfusion for the Rh incompatibility in 1965. Dr. Harrison
did the first surgery for fetal ladder neck obstruction. He
devised a Uterine Stapler which sealed the uterine vessels
and the amnion. This invention allowed intra uterine surgery
to be performed on a regular basis. Dr. Nicolaides has a
huge experience in Fetoscopic laser ablation in Twin to Twin
transfusion syndrome. Intra Uterine fetal surgical
procedures are indicated in those conditions which interfere
with normal development of the fetus and which when
corrected will allow the normal or near normal development
of the fetus.
These procedures are obviously
contraindicated in cases which are incompatible with
postnatal existence or in cases which have severe affliction
or in cases with chromosomal/ genetic syndromes or in cases
associated with other malformations.
Types of Intra Uterine Surgery
The various types of Intra Uterine
Surgery are as follows:-
1) FIGS
2) FETENDO
3) Open Fetal Surgery
4) EXIT
1) FIGS or Fetal image guided surgery
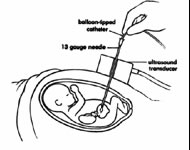
This is the most basic type of Fetal
Surgery, where the procedure is guided by ultrasound image.
The fetus is visualized on ultrasound monitor. The needle is
advanced under vision and the procedure is performed. The
procedures performed are both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Diagnostic
1. Amniocentesis
2. Chorion Villus Sampling
3. Fetal Blood Sampling
4. Fetal skin biopsy
Therapeutic
1. Fetal reduction
2. RFA (Radio Frequency Ablation) of cord in TRAP
3. Placement of Bladder/ Hydrothorax shunts
4. Balloon dilatation in Aortic Stenosis
2) Fetendo or Fetal Endoscopic
Procedure
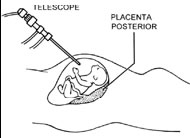
Here, the fetus is observed under
ultrasound vision, a small fetoscope is introduced into the
amniotic cavity. The fetus is observed on both ultrasound
monitor and the fetoscope monitor. This procedure is called
Fetendo because the hand-eye coordination is similar to that
involved in the children's game NINTENDO.
The procedures performed using this
are:-
1. Laser Ablation in TTS
2. Balloon occlusion of Trachea in cases of CDH
3. Cord ligation in acardiac twin
4. Division of Amniotic bands
3) Open Intra Uterine Fetal Surgery
This is usually done in mid trimester.
The mother is anaesthetized and sonography is performed to
map the surface anatomy of the fetus and localize the
placenta. Mother is usually given deep general anesthesia.
This is essential to prevent intra operative uterine
contractions and also to allow manipulation of the fetus. An
appropriate hysterotomy incision is performed. The uterine
stapler is used to seal the vessels and the amnion. Before
surrey top up fetal anesthesia is administered. This
consists of intramuscular injection of Inj Vecuronium and
Inj Fentanyl. The affected fetal part is exteriorized and
operated upon. The amniotic fluid which drains out is
replaced by warm Ringer Lactate solution. The fetus is
monitored using a miniature pulse oxymeter, intra operative
fetal echocardiography and fetal hemoglobin estimation. The
fetus is transfused with O-ve blood to replace for the lost
blood. At the time of closure the mother is administered inj
Magnesium Sulphate along with Indomethacin rectal
suppository for prevention of preterm labour.
The indications are:-
1. Excision of CCAM
2. Repair of meningomyelocoele
3. Excision of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
4) EXIT -Ex Utero Intra Partum
Treatment Procedure
This is performed for those cases where
the baby is likely to have a compromised airway post
delivery. Here the procedure is started as a routine LSCS,
performed with the intention of delivering the baby.
However, it is performed under general anesthesia. The
uterine incision is taken, the baby is delivered. However,
the cord is not clamped allowing the baby to get oxygen from
the mother. A laryngoscope is introduced and intubation is
attempted. In case the intubation is unsuccessful,
tracheotomy is performed and the tube is passed. Either
ways, the airway is secured. The cord is then cut and the
baby is separated from the mother and delivered. As the
airway is secured, the baby can now be placed on a
ventilator and the definitive surgery can be performed at a
later date.
The indications are:-
1. CHAOS (Congenital High Airway
Obstruction Syndrome)
2. CCAM (Congenital cystadenomatoid malformation of the
lung)
3. Removal of balloon implanted in larynx in cases of
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
4. Pulmonary Sequestration
Challenges in Intra Uterine Fetal
Surgery
1) Maternal Risks
• Tocolytic therapy can cause maternal
pulmonary edema
• Subsequent delivery is by LSCS
• Intra operative blood loss
• Amniotic Fluid Leak
• Chorioamnionitis
• Wound infection
• Maternal mirror syndrome causing pulmonary edema in the
mother
• Deep anesthesia is required for intra operative
manipulation ; this can depress
• Maternal, fetal cardiovascular system and placental
circulation.
2) Fetal Risks
• Prematurity
• Intra Uterine infection
• Fetal vascular events like intestinal agenesis and renal
atresia
• Premature closure of Ductus Arteriosus
• Fetal vascular insults due to hypoxia during anesthesia
• Fetal organ system is immature
• Fetal cardiac system is sensitive to heart rate change
• Fetal has high vagal tone and responds to stress with
precipitous bradycardia
• Fetal circulating volume is low, hence is more at risk of
hypovolemia
• Deep maternal anesthesia puts fetus at risk
• Fetus tends to lose heat more easily hence exposed fetal
part places
• Immature fetal coagulation system predisposes the fetus to
intra operative bleeding
3) Ethical Issues
• Not all procedures are performed
regularly
• Results are not always guaranteed
• There are potential risks to mother and fetus
• Should a procedure which is not guaranteed to provide
favorable results (like sacrococcygeal teratoma) be
performed on the insistence of the mother?
• Should a procedure which is guaranteed to perform
favorable results (like CCAM) be not performed on the
refusal of the mother?
• Research on Intra Uterine Fetal surgery is controversial
as there are risks involved to both the mother and the fetus
• Surgical animal models do not always replicate human
conditions
4) Does the fetus feel pain?
Pain is a subjective phenomenon and
hence there is no objective confirmation that the fetus
feels pain. Some researchers have even questioned the
assumption that the fetus feels pain. However, pain or
noxious stimulus is also known to bring about certain
physiological changes. These include release of fetal
cortisol, fetal endorphins as well as initiation of brain
sparing vascular changes. Fetal administration of
anesthetics is known to suppress the release of fetal
cortisol and fetal endorphins. Thus it can be induced that
the fetus does feel pain and this sensation is suppressed at
least to some extent by administration of anesthetics to the
fetus. Fetal pain is also suspected to be the reason for
preterm labour in some cases of intra uterine surgery.
5) Concept of Fetal Consciousness
The issue of intra uterine fetal
surgery raises the question of fetal consciousness. This is
important because the decision for surgery is taken on
behalf of the fetus. Some researchers dismiss idea that
there is fetal consciousness in utero. They say that it is
only after birth that the fetus exists as an individual.
However, some psychologists have proposed that the fetus has
two kinds of "consciousness": one is the Self Consciousness,
where the fetus is observed to respond to accidental needle
prick at the time of amniocentesis and the other one is
Transcendal Consciousness where the fetus is reported to be
aware of its surrounding events.
Future possibilities
1) Deliver stem cells to the fetus
in cases of certain inheritable condition. It is given
through intra-amniotic or intra umbilical venous route.
The advantage is that the fetus does not mount graft v/s
host reaction. The conditions where it has been
attempted are:
2) Intra uterine plastic surgery:
The fetal tissues are known to heal without scarring.
Hence repair of cleft lip and cleft palate has been
attempted in animal experiment. In future, this may
allow repair of these conditions in humans without any
residual sign after birth. Thus fetal surgery is an
exciting field where the possibilities are innumerable:
• Hemoglobinopathies
• Mucopolysaccharidoses
• Mucolipidoses
• Fanconi Anemia
• Immunodeficiency syndromes
• Diamond Blackfan Syndrome
|